Develop Radiant Skin and Stronger Bones with Vitamin C

What is Vitamin C?
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin that our bodies cannot produce and must be obtained from the diet or supplements. It is well-known for its numerous health benefits, including its role in forming blood vessels, cartilage, muscles, and the collagen that supports bones. As we age, maintaining adequate levels of Vitamin C becomes increasingly important for overall health.
With its dual role in maintaining health and enhancing appearance, Vitamin C becomes a standout nutrient as we age. It stimulates collagen production, resulting in firmer, more elastic skin, fading dark spots, and evening-out skin tone for a brighter complexion. Beyond its beauty benefits, Vitamin C is a guardian of our immune system, making it stronger and more resilient. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in maintaining strong bones, ensuring that our body remains as vibrant as our skin looks.
Why Is It Important?
Ascorbic acid plays a major role in skin health, primarily through its involvement in collagen synthesis. Collagen is a key protein that helps keep our skin firm and youthful. Vitamin C aids in repairing damaged skin, reducing the appearance of wrinkles, and may even contribute to wound healing. Its antioxidant properties also protect the skin from harmful UV rays and environmental pollutants (1).
Vitamin C supports the immune system in several ways. It enhances white blood cell activity and serves as a potent antioxidant to neutralize harmful free radicals (2). Free radicals are unstable molecules that can harm cells. Vitamin C fights them by giving them what they need to stabilize, preventing damage to our cells. Additionally, it contributes to collagen synthesis, crucial for maintaining protective barriers in the body. Lastly, Vitamin C promotes antibody production and helps regulate inflammation.
Vitamin C is involved in numerous other bodily functions, including the absorption of iron, which is crucial for preventing anemia (3). Vitamin C also contributes to maintaining healthy gums, teeth, and bones. For adults, maintaining sufficient Vitamin C levels is crucial to ward off deficiency-related health issues, including scurvy, characterized by symptoms like lethargy, skin spots, and bleeding gums.
Vitamin C For Bones
Vitamin C's connection to bone health might not be as well-known as some other vitamins, but it plays a essential role in processes such as collagen synthesis, bone matrix support, and bone remodeling (4). These functions are important for maintaining the strength, flexibility, and overall structural integrity of bones. Additionally, Vitamin C's antioxidant properties act as a shield protecting bone cells from oxidative stress.
Collagen is a crucial protein that serves as a structural framework in different tissues, particularly in bones. Synthesis refers to the process of producing collagen. When bones are formed, a critical step is the creation of a bone matrix, which involves depositing minerals like calcium and phosphate along with collagen fibers. This combination results in a strong and resilient structure that provides bones with their durability and support.
Throughout life, bone tissue undergoes constant turnover. Specialized cells called osteoclasts break down old or damaged bone tissue, while osteoblasts generate new bone. This dynamic process ensures bone strength, adapts to mechanical stresses, and repairs micro-damage. In essence, collagen synthesis, bone matrix formation, and bone remodeling are intricate processes that work in harmony to maintain the structure, strength, and adaptability of our bones throughout life.

Signs & Symptoms of Vitamin C Deficiency
While we often hear about the benefits of Vitamin C, it's equally important to recognize the signs of not getting enough. Vitamin C deficiency symptoms can be subtle at first, but it has significant implications for our health. Some common Symptoms to watch out for:
1
Fatigue and Weakness
Vitamin C deficiency can lead to feelings of fatigue and weakness as the body's ability to produce energy is compromised without an adequate supply of this essential nutrient (5).
2
Joint and Muscle Aches
Insufficient vitamin C intake may result in joint and muscle aches due to its role in collagen synthesis, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of connective tissues supporting joints and muscles (6).
3
Swollen or Bleeding Gums
Vitamin C deficiency can weaken blood vessels, leading to swollen or bleeding gums as a result of impaired collagen production, which is crucial for gum health and repair (7).
4
Dry and Splitting Hair
Vitamin C is necessary for synthesizing collagen, a protein that supports hair structure and health. A deficiency in vitamin C can lead to dry, brittle hair prone to splitting and breakage (8).
5
Depression and Mood Changes
Adequate levels of vitamin C are important for neurotransmitter synthesis and regulation, including serotonin, which plays a key role in mood regulation. Vitamin C deficiency may contribute to symptoms of depression and mood changes.
6
Concentration and Memory Loss
Vitamin C is involved in the production of neurotransmitters essential for cognitive function. A deficiency in vitamin C may impair concentration and memory due to disruptions in neurotransmitter synthesis and function.
More Serious Health Concerns
If left unchecked, Vitamin C deficiency can lead to severe health issues. One of the most well-known consequences is scurvy, a condition rarely seen today but can still occur. Symptoms of scurvy include swollen, bleeding gums, and in advanced stages, tooth loss. Joint pain and poor wound healing are other indicators of seriously low Vitamin C levels.
The Impact on Overall Well-being
Inadequate Vitamin C doesn't just affect physical health; it can impact overall well-being. A lack of this essential nutrient can lead to general malaise and reduced resistance to infections. For adults, maintaining adequate Vitamin C levels is crucial, not just for physical health but for overall quality of life. Being aware of these signs is the first step in addressing Vitamin C deficiency. Simple changes in diet or the inclusion of Vitamin C supplements can effectively reverse these symptoms and restore the body's balance.
Thinking of Trying Ocean Essence?
Ocean Essence provides a healthy balance of bone nourishing minerals and vitamins including Calcium, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Vitamin K.
Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) of Vitamin C
Ever wondered how much Vitamin C you really need? It's not just about loading up on oranges or supplements; it's about understanding the specific needs of your body at different stages of life. Here's a closer look at the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for Vitamin C for various age groups and conditions.
Vitamin C Needs by Age - Infants (0-12 months): For the smallest ones, the exact RDA for Vitamin C isn't set, as breast milk or formula usually meets their needs. - Children (1-18 years): As kids grow, their Vitamin C requirements increase, starting from 15 mg and going up to 75 mg as they approach adulthood. - Adults (19 years and older): When it comes to Vitamin C for adults, the RDA is 90 mg for men and 75 mg for women. This level supports overall health, from immune function to skin health.
Special Considerations: Pregnant Women: Pregnancy ups the ante, with an RDA of 85 mg to support both the mother and the developing baby. Breastfeeding Women: Nursing mothers need even more, about 120 mg, to ensure both their and their baby's needs are met.
Discovering Natural Sources of Vitamin C
Incorporating Vitamin C-rich foods into our diet is a delicious and natural way to meet our daily requirements. From the zesty burst of citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits to the sweet juiciness of strawberries and tropical delights like kiwi, guava, and papaya, nature provides an abundance of options to invigorate our taste buds and nourish our bodies.
Vibrant bell peppers, crunchy broccoli, and leafy greens add variety and depth to our culinary repertoire while packing a punch of this essential vitamin. Exploring these natural sources not only encourages a diverse and colorful diet but also promotes overall health and well-being, ensuring we meet our daily requirements in a delicious and enjoyable way.

Fruits High in Vitamin C
Citrus Fruits: Oranges, grapefruits, lemons, and limes are the poster children for Vitamin C. Squeeze some lemon on your salad or start your day with a glass of fresh orange juice.
Berries: Strawberries, raspberries, and blueberries aren’t just tasty; they're also packed with Vitamin C. Add them to your yogurt, cereal, or enjoy them as a healthy snack.
Tropical Fruits: Pineapples, mangoes, and papayas offer a tropical twist to your Vitamin C intake. They're great in smoothies or as part of a fruit salad.
Vegetables Rich in Vitamin C
Bell Peppers: Red and green bell peppers contain surprisingly high amounts of Vitamin C. Add them to stir-fries, salads, or snack on them raw.
Dark Green Leafy Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are not only rich in Vitamin C but also in other nutrients. Toss them in your salads or sauté them as a side dish.
Broccoli and Brussels Sprouts: These cruciferous vegetables are another excellent source. Steam or roast them to preserve their Vitamin C content.
Tips for Maximizing Vitamin C Intake
Keep Cooking to a Minimum: Vitamin C is sensitive to heat, so light cooking or eating these foods raw helps retain their nutrient content.
Mix and Match: Combine these Vitamin C sources in your meals. Think fruit salads, veggie-packed stir-fries, or smoothies with a mix of fruits and greens.
Get Your OceanEssense Today
Bones are complex, we make it simple.
When Diet Isn't Enough
When Diet Isn't Enough
Even with a well-rounded diet, achieving the recommended levels of Vitamin C solely through food can be challenging. For individuals facing dietary restrictions or limited access to fresh produce, supplements become a valuable ally. They offer a reliable source of this essential nutrient, ensuring that everyone, regardless of dietary constraints, can effortlessly meet their daily Vitamin C requirements.
Ocean Essence goes above and beyond Vitamin C, delivering a bone healing solution by providing optimal calcium and magnesium alongside essential nutrients like Vitamin D, Vitamin K2, boron, copper, manganese, and Silica from bamboo.
Supported by scientific research, these vitamins and minerals play a crucial role in supporting bone health, supporting joint health, and promoting digestive well-being. Our supplements are designed to offer a comprehensive solution for fulfilling your Vitamin C needs, presenting a natural and eco-friendly option to support your wellness journey.

NOTE: It's important to note that while Vitamin C supplements are beneficial, they should complement, not replace, a healthy diet. Whole foods provide a complex array of nutrients and dietary fiber that supplements alone can't offer. Therefore, a balanced approach that includes both natural food sources and vitamin c supplements, when necessary, is ideal for optimal health.







Ocean Essence - Total Bone Support
Support Bone Density*
Product Description:
Ocean Essence - Total Bone Support is an algae-based calcium supplement rich in key vitamins and minerals your bones need. Helps promote bone density.*
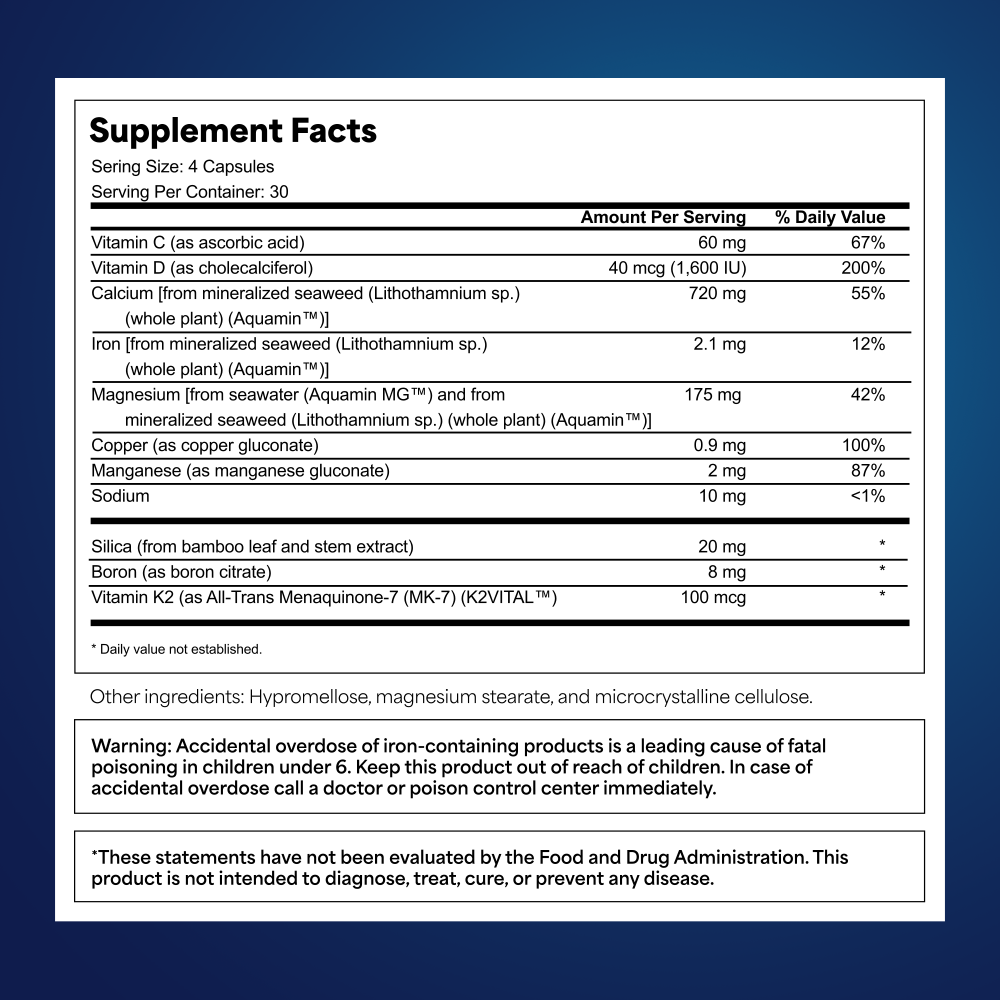
Supplement Facts:

Select Frequency:
Subscribe & Save 15%
Amount:
-
-
-
-
Subscription:
365 Day Money-Back Guarantee
Not satisfied? Get a full refund.*

Manufactured In The USA
Crafted in the USA for superior quality and reliability.

2-5 Day Shipping & Delivery With USPS ground
Experience Fast and Reliable Shipping Nationwide
REVIEWS
References:
(1) Lin, J. Y., Selim, M. A., Shea, C. R., Grichnik, J. M., Omar, M. M., Monteiro-Riviere, N. A., & Pinnell, S. R. (2003). UV photoprotection by combination topical antioxidants vitamin C and vitamin E. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 48(6), 866-874. - https://doi.org/10.1067/mjd.2003.425
Choi, S., Han, J., Kim, J. H., Kim, A. R., Kim, S. H., Lee, W., ... & Kim, Y. S. (2020). Advances in dermatology using DNA aptamer “Aptamin C” innovation: Oxidative stress prevention and effect maximization of vitamin C through antioxidation. Journal of cosmetic dermatology, 19(4), 970-976. -https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13081
(2) Jafari, D., Esmaeilzadeh, A., Mohammadi-Kordkhayli, M., Rezaei, N. (2019). Vitamin C and the immune system. In: Mahmoudi, M., Rezaei, N. (eds) Nutrition and Immunity. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16073-9_5
Carr, A. C., & Maggini, S. (2017). Vitamin C and immune function. Nutrients, 9(11), 1211-. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111211
(3) Lane, D. J. R., & Richardson, D. R. (2014). The active role of vitamin C in mammalian iron metabolism: Much more than just enhanced iron absorption. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 75, 69–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.07.007
(4) Chin, K. Y., & Ima-Nirwana, S. (2018). Vitamin C and bone health: Evidence from cell, animal and human studies. Current drug targets, 19(5), 439-450. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389450116666150907100838
(5) Pearson, J. F., Pullar, J. M., Wilson, R., Spittlehouse, J. K., Vissers, M. C., Skidmore, P. M., ... & Carr, A. C. (2017). Vitamin C status correlates with markers of metabolic and cognitive health in 50-year-olds: findings of the CHALICE cohort study. Nutrients, 9(8), 831. - https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9080831
Ravindran, R. D., Vashist, P., K. Gupta, S., S. Young, I., Maraini, G., Camparini, M., ... & Fletcher, A. E. (2011). Prevalence and risk factors for vitamin C deficiency in north and south India: a two centre population based study in people aged 60 years and over. PLoS One, 6(12), e28588. - https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028588
Johnston, C. S., Barkyoumb, G. M., & Schumacher, S. S. (2014). Vitamin C supplementation slightly improves physical activity levels and reduces cold incidence in men with marginal vitamin C status: A randomized controlled trial. Nutrients, 6(7), 2572-2583. - https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6072572
(6) Boyera, N., Galey, I., & Bernard, B. A. (1998). Effect of vitamin C and its derivatives on collagen synthesis and cross‐linking by normal human fibroblasts. International journal of cosmetic science, 20(3), 151-158. - https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1467-2494.1998.171747.x
Jacob, R. A., & Sotoudeh, G. (2002). Vitamin C function and status in chronic disease. Nutrition in clinical care, 5(2), 66-74. - https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-5408.2002.00005.x
(7) Nachbar, F., & Korting, H. C. (1995). The role of vitamin E in normal and damaged skin. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 73(1), 7-17. - https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00203614
(8) Almohanna, H. M., Ahmed, A. A., Tsatalis, J. P., & Tosti, A. (2019). The role of vitamins and minerals in hair loss: a review. Dermatology and therapy, 9(1), 51-70. - https://doi.org/10.1007/s13555-018-0278-6

