Vitamin D: The Key to Bone Health and Absorption
The Facts
Vitamin D is considered one of the most important vitamins, It not only regulates calcium absorption leading to stronger bones, but also helps the immune system fight threats like infections and viruses (1). It supports muscle movement and is known to regulate mood by maintaining a balanced and positive mental state.
Research suggests that up to 13% and 40% of the population are severely and moderately deficient in Vitamin D (2). If getting your daily dose can be as simple as soaking up some sunshine, then what causes deficiencies? In this blog, we'll explore the critical yet often underestimated role of Vitamin D. We will reveal why it deserves more attention in our health routines and how it can significantly enhance our overall well-being.
What Is Vitamin D & Why Is It Essential To Bone Health?
Vitamin D can be more accurately classified as a prohormone rather than a vitamin. Unlike typical vitamins that solely come from the diet, Vitamin D can be produced by the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight. This natural synthesis involves transformations in the liver and kidneys, converting Vitamin D into an active form that significantly enhances calcium absorption (3).
Without sufficient vitamin D, the body struggles to absorb an adequate amount of calcium from the diet, even if the calcium intake is high (4). This is crucial not only for maintaining strong bones but also for supporting muscle function, nerve transmission, and other vital processes. Inadequate Vitamin D intake can elevate the risk of various diseases, including osteoporosis, rickets, heart diseases, and an increased likelihood of developing cancers, such as breast and prostate cancer, particularly in postmenopausal women.
Benefits Of Vitamin D:
✅ Enhanced Bone Health
One of the most well-known benefits of Vitamin D3 is its role in bone health. It enhances the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, two minerals essential for building and maintaining strong bones (5).
✅ Boosts Immune System
Vitamin D3 is a key player in the immune system. It helps regulate and strengthen the immune response, making it essential in the body's defence against infections and diseases. Adequate levels of Vitamin D3 can help reduce the risk of autoimmune diseases and improve the body's ability to fight off common illnesses (6).
✅ Optimizes Mental Health & Mood Regulation
Emerging research suggests a link between Vitamin D3 and mental health. Adequate levels of this vitamin are associated with a lower risk of depression and may play a role in mood regulation. This is particularly important in regions with limited sunlight exposure, where Vitamin D3 deficiency is more common (7).
✅ Reduces Risk Of Stroke & Heart Diseases
Vitamin D3 also contributes to heart health. It's involved in regulating blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart disease. Maintaining adequate Vitamin D3 levels is a proactive step in promoting overall cardiovascular health (8).
✅ Muscle Function & Weight Management
Beyond bones and immunity, Vitamin D3 is essential for proper muscle function. It helps in muscle contraction and strength, which is crucial for daily activities and physical performance. Vitamin D may also play a role in weight management by influencing appetite, regulating fat cells, improving insulin sensitivity, and reducing inflammation (9).
✅ Supports Cellular Health
Research suggests that maintaining sufficient Vitamin D levels may contribute to inhibiting the development of certain cancers, including prostate, breast, pancreatic and Colorectal cancer. Due to its roles in cellular regulation, immune system support, and inflammation reduction (10).
Supporting Healthy Bone Remodeling
By modulating the activity of osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) and osteoclasts (cells responsible for bone resorption), Vitamin D ensures the equilibrium necessary for skeletal integrity. This nuanced regulatory function is essential in preventing conditions like osteoporosis and fractures, highlighting the nuanced impact of Vitamin D on bone health.
Thinking of Trying OceanEssense?
Ocean Essence provides a healthy balance of bone nourishing minerals and vitamins including Calcium, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Vitamin K.
Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) of Vitamin D
When it comes to Vitamin D, one size doesn't fit all. The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) is like your daily nutrition target, tailored to ensure you're getting just the right amount of this essential nutrient. It's a bit like a nutritionist's version of a daily step count – a goal to aim for optimal health.
The RDA for Vitamin D varies depending on your age, gender, and other individual health factors. It's a bit like a recipe – each person's ingredients (or in this case, nutrient needs) are a little different. These guidelines are there to give you a baseline, but remember, your personal 'recipe' might need some tweaking.
It's wise to consult with a healthcare provider for advice that's customized just for you, especially if you have specific health conditions or concerns. They can help fine-tune your Vitamin D intake, ensuring you're hitting your health goals without overstepping the mark.
RDA Table

Age Group
RDA of Vitamin D (in International Units - IU)
Infants (0-12 months)
400 IU
Children (1-18 years)
600-1,000 IU*
Adults (19-70 years)
600-800 IU
Adults (>70 years)
800 IU
Pregnant/Breastfeeding Women
600-800 IU
Important Notice: The following RDA of Vitamin D is for informational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider.
Identifying Deficiency - Key Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing a Vitamin D deficiency is important, as it often goes unnoticed due to its subtle symptoms. Deficiency can lead to conditions like osteomalacia and rickets, causing weakened bones and heightened fracture risks. Understanding the signs can help in early detection and prevention of serious health issues.
Common Causes Of Deficiency:
1
Fatigue or Tiredness
One of the most common but easily overlooked signs of Vitamin D deficiency is a general feeling of fatigue and tiredness. If you're consistently feeling exhausted without a clear reason, it might be worth checking your Vitamin D levels.
2
Bone Pain or Weakness
Since Vitamin D is vital for bone health, deficiency can lead to bone pain, particularly in the back and joints. This pain might be accompanied by a sense of weakness or discomfort in the bones.
3
Muscle Weakness or Cramps
Alongside bone health, Vitamin D is important for muscle function. A deficiency can manifest as muscle pain, weakness, or cramps, which can sometimes be mistaken for general fatigue or stress.
4
Mood Changes or Lack of Focus
Research links low Vitamin D levels to mood fluctuations, including depression and anxiety. If your mood changes, especially during sunlight-deprived months, Vitamin D levels might contribute. Additionally, a lack of focus can accompany Vitamin D deficiency, impacting your ability to stay attentive and engaged in daily tasks.
Important Notice: Always consult with your healthcare professional before making any changes to your medication regimen or introducing new supplements.
5
Frequent Illness or Infections
If you experience frequent colds or flu, it might signal a weakened immune system from Vitamin D deficiency. Insufficient levels may compromise your body's defense, increasing susceptibility to illnesses. If recurrent sickness is noticed, check Vitamin D levels and consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Common Causes Of Deficiency
Keeping our Vitamin D levels in check is like balancing a diet – a bit of this, a bit of that. A dash of sunlight, a sprinkle of Vitamin D-rich foods, and maybe a supplement or two, just like a recipe for good health.
1
Limited Sun Exposure
In our modern, indoor-oriented lifestyles, limited exposure to sunlight remains a significant contributor to Vitamin D deficiency. Whether due to work demands, climate, or lifestyle choices, reduced time spent outdoors can hinder the body's natural ability to produce Vitamin D through sunlight exposure. This lack of sun-kissed moments underscores the importance of finding a balance between indoor and outdoor activities for overall health.
2
Dietary Insufficiency
While sunlight is a primary source, insufficient dietary intake of Vitamin D can also lead to deficiencies. A diet lacking in fatty fish, fortified dairy products, eggs, and other Vitamin D-rich foods contributes to inadequate Vitamin D levels. Addressing dietary choices is essential for those who may not absorb sunlight efficiently or face limited exposure due to various factors.
3
Darker Skin Pigmentation
Individuals with darker skin pigmentation have a higher melanin content, which acts as a natural sunblock. While this offers protection against harmful UV rays, it also reduces the skin's ability to produce Vitamin D. This nuanced relationship between skin pigmentation and Vitamin D synthesis highlights the need for tailored approaches to sun exposure and dietary supplementation.
4
Age-Related Factors
Age plays a role in Vitamin D metabolism. As people age, the skin becomes less efficient at synthesizing Vitamin D, and dietary intake may decline. Coupled with factors like decreased outdoor activity, age-related changes contribute to a higher risk of Vitamin D deficiency among older individuals. Recognizing these age-related factors is crucial for crafting age-appropriate strategies to maintain optimal Vitamin D levels.
5
Obesity and Body Fat
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin, and excess body fat can sequester Vitamin D, making it less bioavailable. Individuals with obesity face a higher risk of Vitamin D deficiency due to altered metabolism and storage. Addressing the interplay between body fat and Vitamin D absorption is key in developing tailored approaches for those with obesity.
Food and Sources High in Vitamin D
Ensuring adequate vitamin D levels is crucial for overall health, especially for optimal bone health. Fatty fish like salmon, trout, mackerel, and sardines are excellent natural sources of vitamin D, as is cod liver oil, which is available as a supplement. Egg yolks offer a moderate amount of vitamin D, and fortified foods such as milk, orange juice, breakfast cereals, and yogurt provide additional sources. Certain mushrooms exposed to UV light during growth also contain vitamin D. Including these foods in your diet can help maintain adequate vitamin D levels and support well-being.
However, challenges such as limited sun exposure and factors like age and skin pigmentation can impact Vitamin D synthesis, potentially leading to deficiencies. Inadequate Vitamin D levels are associated with weakened bones and an increased risk of conditions like osteoporosis and fractures. Therefore, alongside dietary sources, strategies like sun exposure and supplementation become imperative in maintaining optimal Vitamin D levels for robust bone health and overall well-being.

Get Your OceanEssense Today
Bones are complex, we make it simple.
Enhancing Bone Health Naturally With Ocean Essence
Enhancing Bone Health Naturally With Ocean Essence
From bolstering our immune system to enhancing mental well-being and aiding in weight management, the benefits of Vitamin D are diverse and significant. However, maintaining optimal levels of Vitamin D can be a challenge. Supplements like Ocean Essence can help in bridging the gap between busy lifestyle and the body's needs.
Ocean Essence is designed to, promote bone metabolism, improve joint health, and enhance digestive balance, all with natural ingredients. Containing Calcium, Magnesium, Vitamin D, Vitamin K2 and Vitamin C, and boron, the combination of these vitamins and minerals are backed by scientific research for their role in supporting bone density.



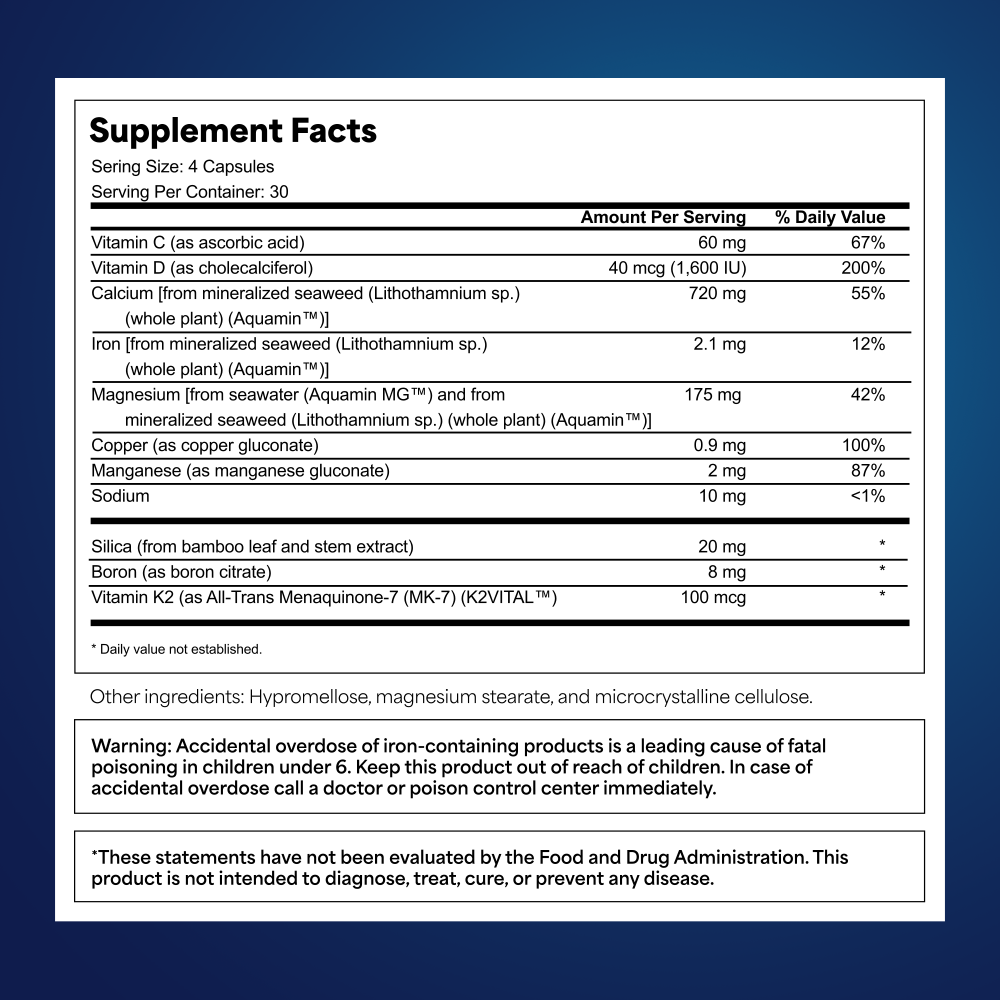





Ocean Essence - Total Bone Support
Support Bone Density*
Product Description:
Ocean Essence - Total Bone Support is an algae-based calcium supplement rich in key vitamins and minerals your bones need. Helps promote bone density.*
Supplement Facts:

Select Frequency:
Subscribe & Save 15%
Amount:
-
-
-
-
Subscription:
365 Day Money-Back Guarantee
Not satisfied? Get a full refund.*

Manufactured In The USA
Crafted in the USA for superior quality and reliability.

2-5 Day Shipping & Delivery With USPS ground
Experience Fast and Reliable Shipping Nationwide
REVIEWS
References:
(1) Kamen, D. L., & Tangpricha, V. (2010). Vitamin D and molecular actions on the immune system: modulation of innate and autoimmunity. Journal of molecular medicine, 88, 441-450. - https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-010-0590-9
(2) Amrein, K., Scherkl, M., Hoffmann, M., Neuwersch-Sommeregger, S., Köstenberger, M., Tmava Berisha, A., Martucci, G., Pilz, S., & Malle, O. (2020). Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: An update on the current status worldwide. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 74(11), 1498–1513. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y
(3) Bikle, D. D. (2014). Vitamin D metabolism, mechanism of action, and clinical applications. Chemistry & Biology, 21(3), 319-329. https://europepmc.org/article/nbk/nbk278935
(4) Christakos, S., Dhawan, P., Porta, A., Mady, L. J., & Seth, T. (2011). Vitamin D and intestinal calcium absorption. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 347(1), 25–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2011.05.038
(5) Trautvetter, U., Neef, N., Leiterer, M., Kiehntopf, M., Kratzsch, J., & Jahreis, G. (2014). Effect of calcium phosphate and vitamin D3 supplementation on bone remodelling and metabolism of calcium, phosphorus, magnesium and iron. Nutrition Journal, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-13-6
(6) Aranow, C. (2011). Vitamin D and the immune system. Journal of Investigative Medicine, 59(6), 881–886. https://doi.org/10.2310/JIM.0b013e31821b8755
(7) Anglin, R. E. S., Samaan, Z., Walter, S. D., & McDonald, S. D. (2013). Vitamin D deficiency and depression in adults: systematic review and meta-analysis. British Journal of Psychiatry, 202(2), 100–107. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.111.106666
(8) Reddy Vanga, S., Good, M., Howard, P. A., & Vacek, J. L. (2010). Role of vitamin D in cardiovascular health. The American Journal of Cardiology, 106(6), 798–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2010.04.042
(9) Dawson-Hughes, B. (2017). Vitamin D and muscle function. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 173, 313–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.03.018
Szymczak-Pajor, I., Drzewoski, J., & Śliwińska, A. (2020). The molecular mechanisms by which vitamin D prevents insulin resistance and associated disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(18), 6644-. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186644
(10) Feldman, D., Krishnan, A. V., Swami, S., Giovannucci, E., & Feldman, B. J. (2014). The role of vitamin D in reducing cancer risk and progression. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 14(5), 342–357. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3691

